3.11 Tables
If you have some data in R and you want to display them as nice tables, you can use knitr::kable(), knitr::kableExtra, or xtable packages.
But if you a table already, you can just copy-and-paste the table into your Rmd file. It can be either in
Markdown table, or
Latex table
Note that Pandoc will preserve raw LaTeX code in Markdown documents when converting the document to LaTeX, so you can use LaTeX commands or environments in Markdown. ↩︎
You may use a fenced code block with the attribute
=latex, e.g.,Do not forget the equal sign before
latex, i.e., it is=latexinstead oflatex.=latextells Pandoc to treat the content as raw LaTeX code.
Cross reference tables
Using bookdown cmd: \@ref(tab:chunk-label).
Note that you must provide caption option in knitr::kable(). Otherwise the table won’t be numbered.
And see Table \@ref(tab:mtcars).
```{r mtcars, echo=FALSE}
knitr::kable(mtcars[1:5, 1:5], caption = "The mtcars data.")
```Refer to the Table 3.1.
| mpg | cyl | disp | hp | drat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mazda RX4 | 21.0 | 6 | 160 | 110 | 3.90 |
| Mazda RX4 Wag | 21.0 | 6 | 160 | 110 | 3.90 |
| Datsun 710 | 22.8 | 4 | 108 | 93 | 3.85 |
| Hornet 4 Drive | 21.4 | 6 | 258 | 110 | 3.08 |
| Hornet Sportabout | 18.7 | 8 | 360 | 175 | 3.15 |
knitr::kable(x, format="pipe") is useful when you want to copy-and-paste R output from console to other document, e.g., markdown.
knitr::kable(mtcars[1:5, 1:5], format = "pipe")
| | mpg| cyl| disp| hp| drat|
|:-----------------|----:|---:|----:|---:|----:|
|Mazda RX4 | 21.0| 6| 160| 110| 3.90|
|Mazda RX4 Wag | 21.0| 6| 160| 110| 3.90|
|Datsun 710 | 22.8| 4| 108| 93| 3.85|
|Hornet 4 Drive | 21.4| 6| 258| 110| 3.08|
|Hornet Sportabout | 18.7| 8| 360| 175| 3.15|3.11.1 knitr::kable
knitr::kable(x, digits, caption=NULL, escape=TRUE) Create tables in LaTeX, HTML, Markdown and reStructuredText.
It adjusts column widths automatically based on content.
captionThe table caption. In order to number the table, mut specify thecaptionargument.formatPossible values arelatex,html,pipe(Pandoc’s pipe tables),simple(Pandoc’s simple tables),rst, andjira.The value of this argument will be automatically determined if the function is called within a knitr document.
If the tables is not rendered properly, you can specify the format manually.
digitsMaximum number of digits for numeric columns, passed toround().col.namesRename columns.escape = TRUEWhether to escape special characters when producing HTML or LaTeX tables.Default is
TRUE, will treat characters literally; special characters will either be escaped or substituted; no special characters will be interpreted.For example,
$is escaped as\$,_is escaped as\_, and\is substituted with\textbackslash{}See Math in rmd tables for examples of using math symbols in rmd tables.
Set
escape = FALSEwhen you have math symbols in the table.It makes sure that the math symbols will be rendered.
Note that you need to escape certain special characters in LaTeX math mode though, e.g., use
\\sigmafor printing \(\sigma\) inkable.- Don’t need to escape
$,^and_in math mode.
- Don’t need to escape
When set to
FALSE, you have to make sure yourself that special characters will not trigger syntax errors in LaTeX or HTML.Common special LaTeX characters include
#,%,&,{, and}. Common special HTML characters include&,<,>, and".They have special meanings and will be treated as format commands instead of literal characters. E.g.,
#will be interpreted as section headers. If you want to print them as literal characters, you need to escape them properly.These can easily lead to errors or unexpected effects when you render your file.
alignColumn alignment: a character vector consisting of'l'(left),'c'(center) and/or'r'(right).By default or if
align = NULL, numeric columns are right-aligned, and other columns are left-aligned.文字列左对齐,数字列右对齐。
If only one character is provided, that will apply to all columns.
If a vector is provided, will map to each individual column specifically.
Missing values (
NA) in the table are displayed asNAby default.If you want to display them with other characters, you can set the option
knitr.kable.NA, e.g.options(knitr.kable.NA = '')in the YAML to hideNAvalues.booktabs = TRUEuse the booktabs package. Default toFALSE.booktabsTrueFALSEColumn separator No vertical lines in the table, you can add via vlineoptionTable columns are separated by vertical lines. Horizontal lines Only has horizontal lines for the table header and the bottom row.
- Use\toprule,\midrule, and\bottomruleUse \hlineRow behavior A line space is added to every five rows by default.
Disable it withlinesep = "".linesep = ""remove the extra space after every five rows in kable output (withbooktabsoption)linesep = c("", "", "", "", "\\addlinespace")default value; empty line space every 5 rows.
# For Markdown tables, use `pipe` format
> knitr::kable(head(mtcars[, 1:4]), format = "pipe")
| | mpg| cyl| disp| hp|
|:-----------------|----:|---:|----:|---:|
|Mazda RX4 | 21.0| 6| 160| 110|
|Mazda RX4 Wag | 21.0| 6| 160| 110|
|Datsun 710 | 22.8| 4| 108| 93|
|Hornet 4 Drive | 21.4| 6| 258| 110|
|Hornet Sportabout | 18.7| 8| 360| 175|
|Valiant | 18.1| 6| 225| 105|
# For Plain tables in txt, `simple` is useful
> knitr::kable(head(mtcars[, 1:4]), format = "simple")
mpg cyl disp hp
------------------ ----- ---- ----- ----
Mazda RX4 21.0 6 160 110
Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 160 110
Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93
Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258 110
Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360 175
Valiant 18.1 6 225 1053.11.1.1 Math in rmd tables
knitr::kable(x, escape=TRUE)
escape=TRUEwhether to escape special characters when producing HTML or LaTeX tables. Refer tokablearguments for more details.- Defaults to
TRUE. - When
escape = FALSE, you have to make sure that special characters will not trigger syntax errors in LaTeX or HTML. E.g., if you don’t escape\, it will cause an error.
- Defaults to
You need to escape backslashes (\) passed into the table data.
Example 1 of escaping special characters:
```{r, echo=FALSE}
library(knitr)
mathy.df <- data.frame(site = c("A", "B"),
b0 = c(3, 4),
BA = c(1, 2))
colnames(mathy.df) <- c("Site", "$\\beta_0$", "$\\beta_A$")
kable(mathy.df, escape=FALSE)
```If your target output is pdf, it is possible to edit Latex table directly in Rmd.
- Don’t enclose in
$$. - Use
\begin{table}and start your table data.
Example 2 of escaping special characters:
library(knitr)
df <- data.frame(
Variable = c("Return", "Variance", "Literal symbols"),
Formula = c("$r_t = \\frac{P_t}{P_{t-1}} - 1$",
"$\\sigma^2 = Var(r_t)$",
"\\$, \\%, \\_, \\#")
)
kable(df, escape = FALSE, booktabs = TRUE)| Variable | Formula |
|---|---|
| Return | \(r_t = \frac{P_t}{P_{t-1}} - 1\) |
| Variance | \(\sigma^2 = Var(r_t)\) |
| Literal symbols | $, %, _, # |
Expected behaviors:
Returnrow → LaTeX math$r_t ...$renders properly.Variancerow → works with superscripts and variance notation.Literal symbolsrow → shows$ % _ #as text in the PDF.
3.11.2 Data frame printing
To show the tibble information (number of row/columns, and group information) along with paged output, we can write a custom function by modifying the print.paged_df function (which is used internally by rmarkdown for the df_print feature) and use CSS to nicely format the output.
https://stackoverflow.com/a/76014674/10108921
Paged df
- https://bookdown.org/yihui/rmarkdown/html-document.html#tab:paged
- https://github.com/rstudio/rmarkdown/issues/1403
---
title: "Use caption with df_print set to page"
date: "2026-01-24"
output:
bookdown::html_document2:
df_print: paged
---When the df_print option is set to paged, tables are printed as HTML tables with support for pagination over rows and columns.
The possible values of the df_print option for the html_document format.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
default |
Call the print.data.frame generic method; console output prefixed by ##; |
kable |
Use the knitr::kable function; looks nice but with no navigation for rows and columns, neither column types.Suggested for pdf output. |
tibble |
Use the tibble::print.tbl_df function, this provides groups and counts of rows and columns info as if printing a tibble. |
paged |
Use rmarkdown::paged_table to create a pageable table; paged looks best but slows down compilation significantly; |
| A custom function | Use the function to create the table |
The possible values of the df_print option for the pdf_document format: default, kable, tibble, paged, or a custom function.
paged print
```{r echo=TRUE, paged.print=TRUE}
ggplot2::diamonds
```
default output
```{r echo=TRUE, paged.print=FALSE}
ggplot2::diamonds
```
kable output
```{r echo=TRUE}
knitr::kable(ggplot2::diamonds[1:10, ])
```Note that kable output doesn’t provide tibble information.
Available options for paged tables:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| max.print | The number of rows to print. |
| rows.print | The number of rows to display. |
| cols.print | The number of columns to display. |
| cols.min.print | The minimum number of columns to display. |
| pages.print | The number of pages to display under page navigation. |
| paged.print | When set to FALSE turns off paged tables. |
| rownames.print | When set to FALSE turns off row names. |
These options are specified in each chunk like below:
For pdf_document, it is possible to write LaTex code directly.
Do not forget the equal sign before latex, i.e., it is =latex instead of latex.
3.11.3 Stargazer
stargazer print nice tables in Rmd documents and R scripts:
Passing a data frame to stargazer package creates a summary statistic table.
Passing a regression object creates a nice regression table.
Support tables output in multiple formats:
text,latex, andhtml.- In
Rscripts, usetype = "text"for a quick view of results.
- In
stargaerdoes NOT work withanovatable, usepander::panderinstead.
3.11.3.1 Text table
Specify stargazer(model, type = "text")
```{r descrptive-analysis-text, comment = ''}
apply(data[,-1], 2, get_stat) %>%
stargazer(type = "text", digits = 2)
```The text output looks like the following.
===============================================
Dependent variable:
---------------------------
delta_infl
-----------------------------------------------
unemp -0.091
(0.126)
Constant 0.518
(0.743)
-----------------------------------------------
Observations 203
R2 0.003
Adjusted R2 -0.002
Residual Std. Error 2.833 (df = 201)
F Statistic 0.517 (df = 1; 201)
===============================================
Note: *p<0.1; **p<0.05; ***p<0.01Significance codes are shown in the footnote.
By default,
stargazeruses***,**, and*to denote statistical significance at the one, five, and ten percent levels (* p<0.1; ** p<0.05; *** p<0.01).In contrast,
summary.lmuses* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p< 0.001.You can change the cutoffs for significance using
star.cutoffs = c(0.05, 0.01, 0.001).
There is one empty line after each coefficient, to remove the empty lines, specify no.space = TRUE.
The regression table with all empty lines removed:
===============================================
Dependent variable:
---------------------------
delta_infl
-----------------------------------------------
unemp -0.091
(0.126)
Constant 0.518
(0.743)
-----------------------------------------------
Observations 203
R2 0.003
Adjusted R2 -0.002
Residual Std. Error 2.833 (df = 201)
F Statistic 0.517 (df = 1; 201)
===============================================
Note: *p<0.1; **p<0.05; ***p<0.013.11.3.2 HTML table
HTML table can be obtained by specifying stargazer(model, type = "html").
Note that you need to specify results="asis" in the code chunk options. This option tells knitr to treat verbatim code blocks “as is.” Otherwise, instead of your table, you will see the raw html or latex code.
- Note that
*’s do NOT show properly in html output, see Fig. 3.10, need to specify in the footnote (notes) manually.
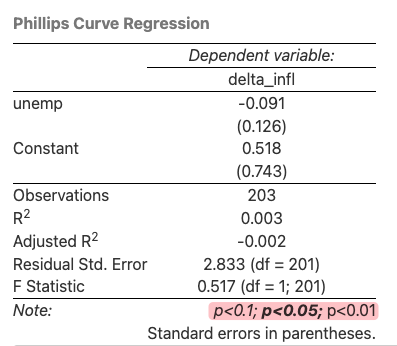
Figure 3.10: Failed to show significance codes in HTML output.
Use the following code to display the correct significance symbols.
```{r descrptive-analysis-html, results="asis"}
# the following code fixes the significance codes in html output
apply(data[,-1], 2, get_stat) %>%
stargazer(
type = "html", digits = 2,
notes = "<span>*</span>: p<0.1; <span>**</span>: <strong>p<0.05</strong>; <span>***</span>: p<0.01 <br> Standard errors in parentheses.",
notes.append = F
)
```*is the HTML entity code for*.- Stargazer by default using
*for 10% significance,**for 5% significance, and***for 1% significance.
After correcting the significance codes, the output looks like Fig. 3.11.
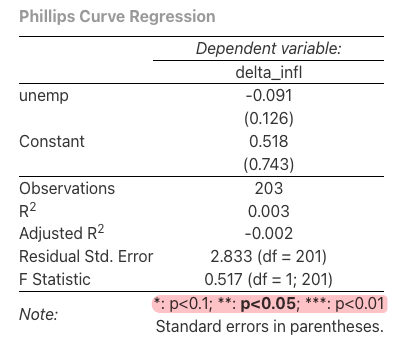
Figure 3.11: Correct significance codes.
3.11.3.3 Common arguments
Table general formatting options:
type = "latex" | "html" | "text"specify output table format.digits = 3an integer that indicates how many decimal places should be used. Defaults to 3 digits.A value of
NULLindicates that no rounding should be done at all, and that all available decimal places should be reported.notesa character vector containing notes to be included below the table.notes.append = FALSEa logical value that indicates whethernotesshould be appended to the existing standard note(s) associated with the table’sstyle(typically an explanation of significance cutoffs).- Defaults to
TRUE. - If the argument’s value is set to
FALSE, the character strings provided innoteswill replace any existing/default notes.
- Defaults to
notes.align:"l"for left alignment,"r"for right alignment, and"c"for centering. This argument is not case-sensitive.
Control structure of regression tables
intercept.bottom = TRUEplace the intercept at the bottom of the table. Defaults toTRUE.keep.stat = NULL: control which model statistics should be kept in the table. Possible values include"n","rsq","adj.rsq","f","ser","ll","aic","bic", and"logLik".- The default is
NULL, which means that all available statistics will be included in the table. - To exclude all statistics, set
keep.stat = c(). - To include only the number of observations and the adjusted R-squared, set
keep.stat = c("n", "adj.rsq").
- The default is
order = NULL: a vector of regular expressions (or of numerical indexes) that indicates the order in which variables will appear in the output.This options is useful when you want to rearrange the order of variables in the regression table.
The order of variables when you include interaction terms might not be what you expect. In my case, the interaction term appears in between the main effects, while I want it to appear after all main effects.
You can use
stargazer(model)to examine the default order and names of variables. Then you can specify the order you want. By default, intercept is at the bottom.Two ways to specify the order:
Regular expression to match variable names.
In order to exactly match the variable names, you can use
vars.order <- c("x1", "x2", "x3", "x3:x1") stargazer(fit1, fit2, fit3, align = TRUE, table.placement = "H", omit.stat = c("f", "ser"), order = paste0("^", vars.order , "$") # format as regular expressions )Note that
^and$are used to exact match the whole variable name. A character vector of all variable names won’t work, asorderexpects regular expressions.A caveat is that you might have some issues if the variable names include special characters, e.g.: “.” or “*“.
Numerical indexes of the variables in the model summary.
stargazer(fit1, fit2, fit3, align = TRUE, table.placement = "H", omit.stat = c("f", "ser"), order = c(2, 3, 1, 4, 5) )This approach is simple, but less readable.
Make your model names more informative:
column.separatea numeric vector that specifies howcolumn.labelsshould be laid out (grouped) across regression table columns.A value of
c(2, 1, 3), for instance, will apply the first label to the two first columns, the second label to the third column, and the third label will apply to the following three columns (i.e., columns number four, five and six).dep.var.labelslabels for dependent variables.column.labelsa character vector of labels for columns in regression tables.This is useful to denote different regressions, informing the name/nature of the model, instead of using numbers to identify them.
When you add custom column labels, you may want to use:
model.numbers = FALSEto suppress the default model numbers (1) (2)…covariate.labelslabels for covariates in the regression tables.Can provide latex symbols in the labels, need to escape special symbols though.
add.linesadd a row(s) for additional info, such as reporting fixed effects.
Make your table more compact:
single.row = TRUEto put coefficients and standard errors on same lineno.space = TRUEto remove the spaces after each line of coefficientsfont.size = "small"to make font size smaller
Tip: Add a blank line under the stargazer table: with a blank line above and below.
3.11.3.4 Cross reference stargazer tables
In pdf output, use
Table \@ref(tab:reg-table)orTable \ref{tab:reg-table}.Table \@ref(tab:reg-table) summarize the regression results in a table. ```{r, include=TRUE, results='asis'} stargazer(capm_ml, FF_ml, type='latex', header=FALSE, digits=4, no.space = TRUE, title="Regression Results for META", label = "tab:reg-table") ```❗️ Note that you need to specify
results="asis"in the code chunk options. Omitting this options will result in failing to compile tex.header=FALSEis to suppress the% Table created by stargazerheader. This applies to onlylatextables.label="tab:reg-table"is to specify the cross reference label for the table.table.placement = "H"set float toHto fix positions. Places the float at precisely the location in the code. This requires thefloatLaTeX package. Remember to load it in the YAML.Defaults to
"!htbp".The
htbpcontrols where the table or figure is placed. Tables and figures do not need to go where you put them in the text. LATEX moves them around to prevent large areas of white space from appearing in your paper.h(Here): Place the float here, i.e., approximately at the same point it occurs in the source text (however, not exactly at the spot)t(Top): Place the table at the top of the current pageb(Bottom): Place the table at the bottom of the current page.p(Page): Place the table at the top of the next page.!: Override internal parameters LaTeX uses for determining “good” float positions.
align = FALSEa logical value indicating whether numeric values in the same column should be aligned at the decimal mark in LaTeX output.
In html output, cross references to stargazer tables are NOT so straightforward.
labeloption instargazerdoes not work. Cannot use chunk labels either.```{r fit-age, echo=FALSE, results='asis', fig.cap="Logistic regression of CHD on age."} # Use title caption from fig.cap tit <- knitr::opts_current$get("fig.cap") # Adding caption for html output tit_html <- paste0( '<span id="tab:', knitr::opts_current$get("label"),'">(#tab:', knitr::opts_current$get("label"), ')</span>', tit) stargazer::stargazer(fit.age, label = paste0("tab:", knitr::opts_current$get("label")), title = ifelse(knitr::is_latex_output(), tit, tit_html), type = ifelse(knitr::is_latex_output(),"latex","html"), notes = "<span>*</span>: p<0.1; <span>**</span>: <strong>p<0.05</strong>; <span>***</span>: p<0.01 <br> Standard errors in parentheses.", notes.append = F, header = F ) ``` Here is another reference to stargazer Table \@ref(tab:fit-age).Don’t change things unless it is absolutely necessary. Run the code chunk before compiling the whole website. It gets slowly as the website gets larger.
stargazer::stargazer()the::is necessary, andheader=Fis necessary and should be place at the end, otherwise will have errors as follows.Error in `.stargazer.wrap()`: ! argument is missing, with no default Backtrace: 1. stargazer::stargazer(...) 2. stargazer:::.stargazer.wrap(...) Execution halted Exited with status 1.Another example if you don’t need to add footnotes.
```{r mytable, results='asis', fig.cap="This is my table."} # Use title caption from fig.cap tit <- knitr::opts_current$get("fig.cap") # Adding caption for html output tit_html <- paste0('<span id="tab:', knitr::opts_current$get("label"), '">(#tab:', knitr::opts_current$get("label"), ')</span>', tit) stargazer::stargazer( fit.age, label = paste0("tab:", knitr::opts_current$get("label")), title = ifelse(knitr::is_latex_output(), tit, tit_html), type = ifelse(knitr::is_latex_output(),"latex","html"), header = F ) ``` Here is a reference to stargazer Table \@ref(tab:mytable).
Alignment of Stargazer Tables
In PDF, the tables will be in the center by default.
However, when working with HTML output, you need to add CSS styling to adjust the table.
References:
3.11.4 xtable
Two steps:
- convert to
xtableobject - print to LaTeX or html code
xtable converts an R object to an xtable object, which can then be printed as a LaTeX or HTML table.
xtable() arguments
alignCharacter vector of length equal to the number of columns of the resulting table, indicating the alignment of the corresponding columns. Also,"|"may be used to produce vertical lines between columns in LaTeX tables, but these are effectively ignored when considering the required length of the supplied vector.- If a character vector of length one is supplied, it is split as
strsplit(align, "")[[1]]before processing. Since the row names are printed in the first column, the length ofalignis one greater thanncol(x)ifxis adata.frame. - Use
"l","r", and"c"to denote left, right, and center alignment, respectively. - Use
"p{3cm}"etc. for a LaTeX column of the specified width. For HTML output the"p"alignment is interpreted as"l", ignoring the width request. Default depends on the class ofx.
- If a character vector of length one is supplied, it is split as
captionCharacter vector of length 1 or 2 containing the table’s caption or title. If length is 2, the second item is the “short caption” used when LaTeX generates a “List of Tables”.digitsNumeric vector of length equal to one (in which case it will be replicated as necessary) or to the number of columns of the resulting table or matrix of the same size as the resulting table, indicating the number of digits to display in the corresponding columns.
print.xtable() arguments
include.rownamesA logical value indicating whether the row names ofxshould be printed. Default isTRUE.typePossible values are"latex"and"html". Default is"latex".
Print a data frame
library(xtable)
df <- data.frame(
Asset = c("A", "B"),
Mu = c(0.175, 0.055),
Sigma = c(0.258, 0.115)
)
# Convert to xtable
xtab <- xtable(df, caption = "Asset Parameters", digits = 3)
# Print html code
print(xtab, type = "html", include.rownames = TRUE)| Asset | Mu | Sigma | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 0.175 | 0.258 |
| 2 | B | 0.055 | 0.115 |
Print a regression table
model <- lm(mpg ~ hp + wt, data = mtcars)
xtab_model <- xtable(model, caption = "Regression of mpg on hp and wt")
# Print as html
print(xtab_model, type = "html", digits = 3)| Estimate | Std. Error | t value | Pr(>|t|) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 37.2273 | 1.5988 | 23.28 | 0.0000 |
| hp | -0.0318 | 0.0090 | -3.52 | 0.0015 |
| wt | -3.8778 | 0.6327 | -6.13 | 0.0000 |
3.11.5 kableExtra
The kableExtra package is designed to extend the basic functionality of tables produced using knitr::kable().
kableExtra::kbl() extends knitr::kable(), with some additional features.
# pipe kabe output to the styling function of kableExtra
kable(iris) %>%
kable_styling(latex_options = "striped")kableExtra::kable_styling(bootstrap_options = c("striped", "hover"), full_width = FALSE)
bootstrap_optionsA character vector for bootstrap table options. Please see package vignette or visit the w3schools’ Bootstrap Page for more information. Possible options includebasic,striped,bordered,hover,condensed,responsiveandnone.stripedalternating row colorshoverUse the:hoverselector ontr(table row) to highlight table rows on mouse over.
full_widthATRUEorFALSEvariable controlling whether the HTML table should have 100% the preferable format forfull_width. If not specified,TRUEfor a HTML table , will have full width by default but- this option will be set to
FALSEfor a LaTeX table.
latex_optionsA character vector for LaTeX table options, i.e., won’t have effect on html tables.Possible options:
Arguments Meanings stripedAdd alternative row colors to the table. It will imports LaTeXpackagexcolorif enabled.scale_downuseful for super wide table. It will automatically adjust the table to fit the page width. repeat_headeronly meaningful in a long table environment. It will let the header row repeat on every page in that long table. hold_position“hold” the floating table to the exact position. It is useful when the LaTeXtable is contained in atableenvironment after you specified captions inkable(). It will force the table to stay in the position where it was created in the document.HOLD_positionA stronger version of hold_position. Requires the float package and specifies [H].
Rows and columns can be grouped via the functions pack_rows() and add_header_above(), respectively.
scroll_box(width = "100%", height = "500px") let you create a fixed height table while making it scrollable. This function only works for html long tables.
# commonly used settings
table %>%
knitr::kable(digits = 5) %>%
kable_styling(bootstrap_options = c("striped", "hover"), full_width = FALSE, latex_options="scale_down") %>%
scroll_box(width = "100%", height = "500px")# escape=TRUE, this makes your life easier, will output the table exactly as it is
result <- read_csv("~/Documents/GDP/data/reg_result/IFE_result.csv")
result %>%
knitr::kable(digits = 5, escape=T) %>%
kable_styling(bootstrap_options = c("striped", "hover"), full_width = FALSE, latex_options="scale_down")# escape=FALSE, have to specify escape by replace `*` to `\\\\*`
result <- read_csv("~/Documents/GDP/data/reg_result/IFE_result.csv")
result <- result %>%
mutate(pval.symbol = gsub("[*]", "\\\\*", pval.symbol) )
result %>%
knitr::kable(digits = 5, escape=FALSE) %>%
kable_styling(bootstrap_options = c("striped", "hover"), full_width = FALSE, latex_options="scale_down")3.11.5.1 tables in pdf output
reg_data %>%
select(Date, adjusted, eRi, rmrf) %>%
head(10) %>%
knitr::kable(digits = c(0,2,4,4), escape=T, format = "latex", booktabs = TRUE, linesep = "" ) %>%
kable_styling(latex_options = c("striped"), full_width = FALSE, stripe_color = "gray!15")knitr::kable() arguments
format = "latex"specifies the output format.align = "l"specifies column alignment.booktabs = TRUEis generally recommended for formatting LaTeX tables.linesep = ""prevents default behavior of extra space every five rows.
kableExtra::kable_styling() arguments
position = "left"places table on left hand side of page.latex_options = c("striped", "repeat_header")implements table striping with repeated headers for tables that span multiple pages.stripe_color = "gray!15"species the stripe color using LaTeX color specification from the xcolor package - this specifies a mix of 15% gray and 85% white.
linebreak(x, align = "l", double_escape = F, linebreaker = "\n") Make linebreak in LaTeX Table cells.
align="l"Choose from “l”, “c” or “r”. Defaults to “l”.
3.11.5.2 Customize the looks for columns/rows
kableExtra::column_spec(kable_input, column) this function allows users to select a column and then specify its look.
# specify the width of the first two columns to be 5cm
table %>%
knitr::kable() %>%
column_spec(1:2, width = "5cm") kable_input: Output ofknitr::kable()column: A numeric value or vector indicating which column(s) to be selected.E.g., to format the 1st and 3rd columns:
column_spec(c(1, 3), width = "5cm").
row_spec() works similar with column_spec() but defines specifications for rows.
- For the position of the target row, you don’t need to count in header rows or the group labeling rows.
row_spec(row = 0, align='c')specify format of the header row. Here I want to center align headers.
3.11.5.3 Add header rows to group columns
add_header_above(): The header variable is supposed to be a named character with the names as new column names and values as column span.
For your convenience, if column span equals to 1, you can ignore the =1 part so the function below can be written as add_header_above(c("", "Group 1" = 2, "Group 2" = 2, "Group 3" = 2)).
kbl(dt) %>%
kable_classic() %>%
add_header_above(c(" " = 1, "Group 1" = 2, "Group 2" = 2, "Group 3" = 2))You can add another row of header on top.
3.11.5.4 Group rows
collapse_rows will put repeating cells in columns into multi-row cells. The vertical alignment of the cell is controlled by valign with default as “top”.
- Not working for html output.
collapse_rows_dt <- data.frame(C1 = c(rep("a", 10), rep("b", 5)),
C2 = c(rep("c", 7), rep("d", 3), rep("c", 2), rep("d", 3)),
C3 = 1:15,
C4 = sample(c(0,1), 15, replace = TRUE))
kableExtra::kbl(collapse_rows_dt, align = "c") %>%
kable_paper(full_width = F) %>%
column_spec(1, bold = T) %>%
collapse_rows(columns = 1:2, valign = "top")Empty string as column name in tibble: use setNames or attr
df <- tibble(" "=1)
setNames(df, "")
# # A tibble: 1 x 1
# ``
# <dbl>
# 1 1
attr(df, "names") <- c("")footnote() add footnotes to tables.
- There are four notation systems in
footnote, namelygeneral(no prefix for footnotes),number,alphabetandsymbol.
3.11.6 huxtable
huxtable supports export to LaTeX, HTML, Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Powerpoint, RTF and Markdown.
library(tidyverse)
library(huxtable)
df <- data.frame(
Parameter = c("\\( \\mu \\)", "\\( \\sigma^2 \\)"),
Boeing = c(0.149, 0.069),
Microsoft = c(0.331, 0.136)
)
ht <- as_hux(df)
ht <- ht %>%
insert_row("\\( \\rho \\)(Boeing, Microsoft)", -0.008, "", after=3) %>%
merge_cells(4, 2:3) %>%
set_align(4, 2:3, "center") %>%
set_bold(1, everywhere, TRUE) %>%
set_width(0.6)
# print_latex(ht) # uncomment this line if printing as LaTeX table
print_html(ht) # print as HTML table| Parameter | Boeing | Microsoft |
|---|---|---|
| \(\mu\) | 0.149 | 0.331 |
| \(\sigma^2\) | 0.069 | 0.136 |
| \(\rho\)(Boeing, Microsoft) | -0.008 | |
as_hux()convert a data frame to ahuxtableobject.insert_row(..., after)insert a new row after the specified row number.Need to provide values for all columns. Empty values can be filled with
"".Table header as row 1
- insert a new row 3 would be
after = 3. - insert as the first row would be
after = 0.
- insert a new row 3 would be
merge_cells(row, col)merge cells in the specified rows and columns.set_align(row, col, value)set alignment for the specified rows and columns.set_align("center")set all cells to be center aligned.
set_width(value)set the width of the table. Default html tables are 100% width.A numeric width is treated as a proportion of f the surrounding block width (HTML) or text width (LaTeX).
col_width(ht, value)set relative widths for each column.Math symbols works fine for bookdown, but not for xaringan presentations.
- By default, huxtable will escape special characters in your cells.
To display special characters such as LaTeX maths, set the
escape_contentsproperty toFALSE.Alternatively, manually escape special characters.
Use
\\( \\mu \\),\\$does not work.
- For xaringan, use unicode symbols instead, e.g.,
μfor\mu,σfor\sigma, andρfor\rho.
- By default, huxtable will escape special characters in your cells.
Example with math symbols in huxtable:
set_escape_contents(FALSE)to turn off escaping special characters.- Set code chunk option
results='asis'to print the table as is. - Escape backslash
\with another backslash\\.
# set escape_contents to FALSE
df <- data.frame(
Parameter = c("$\\mu$", "$\\sigma^2$"),
Boeing = c(0.149, 0.069),
Microsoft = c(0.331, 0.136)
)
ht <- as_hux(df) %>%
set_escape_contents(FALSE) %>% # turn off escaping special characters
set_align("center") %>% # center align all cells
set_bold(1, everywhere, TRUE) %>% # bold header row
set_width(0.6) # set table width
print_html(ht)| Parameter | Boeing | Microsoft |
|---|---|---|
| \(\mu\) | 0.149 | 0.331 |
| \(\sigma^2\) | 0.069 | 0.136 |
In xaringan presentations, use unicode symbols instead of LaTeX math symbols.
- In xaringan presentations, table width is automatically adjusted to fit contents.
- In html output, table width is 100% by default.
```{r results='asis'}
# Create huxtable and use special characters that will be converted to math
df <- data.frame(
Parameter = c("μ", "σ²"),
Boeing = c(0.149, 0.069),
Microsoft = c(0.331, 0.136)
)
ht <- as_hux(df)
ht <- ht %>%
insert_row("ρ(Boeing, Microsoft)", -0.008, "", after=3) %>%
merge_cells(4, 2:3) %>%
set_width(0.6) %>%
set_bold(1, everywhere, TRUE) %>%
set_align(everywhere, everywhere, "center")
print_html(ht)
```will be render as:
| Parameter | Boeing | Microsoft |
|---|---|---|
| μ | 0.149 | 0.331 |
| σ² | 0.069 | 0.136 |
| ρ(Boeing, Microsoft) | -0.008 | |